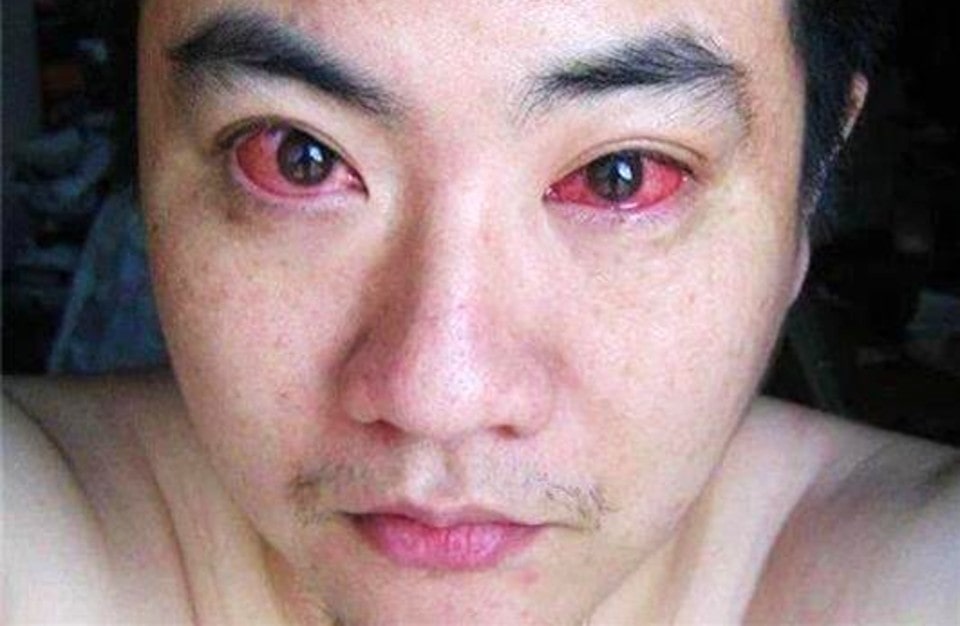
The 40-year-old man went to the hospital after observing that his eyes had been always red and that his vision had become blurry for a while; sadly, he was given an immediate diagnosis of eye cancer.
Numerous scientific research have suggested that the green light from mobile phone screens can kill human retinal cells, which not only affects our eyesight but can also result in more severe disorders.
The light rays from our mobile phones will immediately hit your eye when you utilize them in a dim or dark place. The eye tissue will take longer to dry as a result. This has the potential to cause blindness or eye cancer in the long term.
According to the image above, the man used his cellphone every night before bed for 30 minutes in the dark.
The term “eye cancer” is a general one that covers a wide range of malignancies that can appear in different parts of the eye. A tumor develops when normal cells in or near the eye alter and expand out of control.
A tumor might be benign or cancerous. An unproliferating tumor that has the potential to grow is referred to as a “benign tumor.” A tumor that has the potential to enlarge and spread to different parts of the body is considered malignant.
Cancer that originates in the eyeball is referred to as an intraocular (inside the eye) malignancy.
Ophthalmologists, sometimes known as “eye MDs,” are doctors who focus on conditions affecting the eyes and how they work.
These professionals can identify and treat intraocular melanoma (see below). An optometrist is a different kind of eye doctor. They advise using contacts and eyeglasses. They are not medical professionals and lack the training necessary to treat intraocular cancer.
Eyes and their components
The eye is a light-collecting organ that transmits commands to the brain so that it can create images. The three main parts of the eye are as follows:
Eyeball
Sphere of influence (eye socket)
The eyelid and tear glands are examples of adnexal (accessory) structures.
The eye’s outer layer is made up of the sclera, retina, and uvea. The sclera is the outside layer of the eyeball. Information is sent from the eye to the brain through the retina, a layered tissue that lines the interior of the eyeball. The uvea is in charge of feeding the eye. Both the retina and the uvea have blood arteries.
The uvea is made up of the following components:
The iris is the eye’s colored area that regulates the amount of light that enters the eye.
Ciliary body: Muscular tissue that produces the watery fluid in the eye and aids in eye focus.
The choroid, a layer of tissue beneath the retina that supplies the inside of the eye, is made up of connective tissue and pigmented (coloured) cells called melanocytes. The choroid is the area where tumors are most frequently found.
Various types of intraocular cancer exist.
The most common intraocular cancer in adults is uveal metastases, or cancer that has spread to the uvea from another region of the body. “Secondary cancer” is the term used for this.
The primary intraocular cancer discussed on this page started in the eye and did not spread to other body areas.
Melanoma is the major intraocular cancer that affects people the most frequently. Melanocytes, or skin cells, begin to multiply uncontrollably at this point. Intraocular melanoma is also known as uveal melanoma.
People who have ocular cancer may encounter the following signs or symptoms. Patients with eye cancer still might not show any of these signs. As an alternative, conditions other than cancer may be to blame for these symptoms.
Having impaired vision
One loses some of their field of view.
Observing bursts of light
There are apparent spots, squiggly lines, or floating things (floaters)
A black spot on the iris’ surface. Iris melanoma is distinguishable from choroidal and ciliary body melanoma because it presents as dark patches on the eye.
If you have questions about any of the signs or symptoms on this list, please contact your doctor.
Your doctor will also ask you how often and for how long you’ve been having the symptom in addition to other questions. This will help with the diagnosis—the process of identifying the condition’s root cause.
In the event that cancer is found, symptom alleviation is a crucial part of care and therapy. This sort of treatment is referred to as supportive care, palliative care, and symptom management.
Make an appointment with your doctor to go over any symptoms you are experiencing, particularly any symptoms that are new or changing.